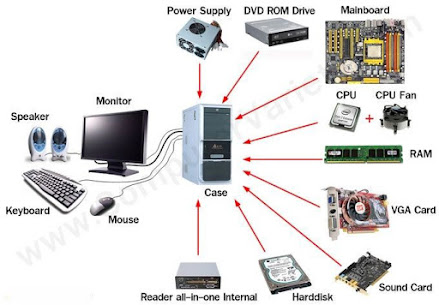
DOS
The full name of dos is Disk operating system. This is the most popular disk operating system which is applied in Micro computer. Dos developed by Tim Pitterson 1981 named 86-Dos.Then in July 1981, Microsoft purchased all right to 86-dos, made substantial alternations to it, Ms. Dos as its primary operating system was released in the year 1981. (Named Ms. Dos 1.0)
When Micro Computer with hard disk was developed in 1983, Ms. Dos 2.0 came in to the market. In 1984, Ms. Dos 3.0 and Ms. Dos 4.0 version were developed.
The latest version of Ms. Dos is Ms. Dos 7.1.
Loading of in to main memory involves of their essential files of dos such as IO. Sys, MS-DOS. Sys, Command.Com in to the main memory. Loading these files in to main memory is called booting.
On↓RAM↓BIOS [Basic Input-Output System]↓POST [Power on Self Test]↓Loads dos on to the memory↓Dos Prompt
When you switch on the computer. First the BIOS present in its permanent memory tests all the devices. This process is called POST (Power on Self Test) after that the operating system present on the disk is stored in the Dos memory (RAM) and with it the main files of Ms. Dos are executed these files are-
- IO. Sys
- Command.Com
- Ms-Dos. Sys
- Autoexec.Bat
- Config. Sys
- HIMEM. Sys etc
Having loaded the Dos in Ram in the disk, it displays a prompt on the screen, which tells that the system is ready to take instructions from you. This prompt is a way to use the efficiency of Dos. You type your command on this prompt. This command prompt is display in the following way
C:\>_
C: - Name of Current Drive
\ - Name of current Directory
> - End of the Prompt
_ - Cursor
File name in Dos
To decide the file name of file, these are the following rules-
[I] There can be two parts of a file name-
(a) Primary Name
It can be given in maximum 8 characters. Such as Sales, Purchase etc.
(b) Extension
It maximum, can be fixed 3 characters.
(II) Dot (.) is used between, primary file name and extension.
(III) No blank space can be given between the letters of the computer file name.
(IV) File name of two are more files cannot be similar.
(V) The command of Ms. Dos can’t be used as file name.
(VI) Special symbol can’t be used as file names, such as -, [, ] , /, <, > etc.
Dos commands are two types-
These commands are always available with dos because these commands are automatically stored in the memory at time of booting. All these commands are collected in command.Com program file. Internal commands are DIR, REN,VER etc.
Eternal command are such short program which are stored either on floppy disk or hard disk and if need be, they are executed and stored in the memory. External Commands are-PROMPT, CHKDSK, EDIT etc.
Internal commands of Dos
Syntax- C :\> VER
Syntax- C :\> VOL
DATE This command displays the current data and enables you to reset it
Syntax- C :\> DATE
Syntax- C :\> TIME
Syntax- C :\> TIME
Syntax- C :\> CLS
Syntax- C:\> Copy Con <File name>
Example- C:\> Copy Con NIST
After typing the matter we save the file press Ctrl +Z key combination or F6 function key.
Syntax- C:\> Type <File name>
Example- C:\> Type NIST
Syntax- C:\> REN <Old file name> <New file name>
Example-C:\> Copy NIST NIST4
Syntax- C:\> COPY <Path of source file name> <Path of target file name>
Example-C:\> Copy C:\> NIST D:\ NIST5
Syntax- C:\> Del <File name>
Example- C:\> Del NIST
Syntax- C :\> PROMPT <Prompt Name> or <$Character>
Valid characters for prompt command are given below-
Characters Value they give
$q =
$$ $
$T Current system time
$D Current system date
$P Current working directory (e.g. - C:\>
$G >
$L <
$V Version number
$N Default drive
$B !
Example-
(2) C :\> Prompt $P$G Output- C:\>
The computer pays attention to only on drive at time. If you want your computer to work in another drive type the name of the drive and the color after it-
Example- C:\>D: Output- D:\>
- Dir also lists the drive volume label and volume serial no.
- Display the files and directory name.
- Display files and directory creation date and creation time.
- Display size of files in byte.
- Display number of files and directories in the list.
- Display total space in byte occupied by the files.
We can add switches the list in different ways. The dir commands with switches are as follows-
DIR/W All the files and directories the root directories will be display width wise.
DIR/S Lists the directories with their sub-directories & files.
DIR/L Display the files & directories name lists in lower case.
DIR/A Display all types of files (hidden system read-only & normal) in directory listing.
DIR/B Display the files and directory name list only.
DIR/Y Display the files & directory listing creation date year in four digits.
DIR/ON Display the lists directories & file in alphabetical order (A to Z).
DIR/O-N Display the list directories & file in a reverse alphabetically order largest size.
DIR/OS Display the files and directories listing by smallest to largest size.
DIR/O-S Display the files and directories listing by largest to smallest.
DIR/OD Display the files & directories listing by oldest to newest date.
DIR/O-D Display the files and directories listing by newest to oldest date.
DIR/AH Display the list of hidden file.
DIR/AS Display the list of system file.
DIR/AR Display the list of read only files.
Wild Card Characters
Two special characters “?”(Question Mark) & “*”(asterisk) are called will cards in dos similar groups of files are to be copied or deleted this wild cards can be used.
Question wild card is used to introduce one character in the file name. If you want to name a list of those files in (drive) which has 6 characters and their extension name is.EXE. Type the following command-
C :\> Dir ?????? . Exe
Asterisk wild card is use to display a group of letters in the file name. Support you want to make a list of those files which have their extension name. Exes you will have to type the following command-
C :\> Dir *.EXE
Syntax-C:\> MD <Directory Name>
Example-C:\> MD NIST
Syntax- C:\> CD <Directory Name>
Example- C:\> CD NIST
CD.. Makes the parent directory of working directory.
CD\ Makes the root directory as the current working directory.
RD This command is used to remove the directory.
Syntax- C:\> RD <Directory name>
Example-C:\> RD NIST
External Command of Dos
EDIT This command is used to edit the already create file by using copy con command and create a new file.
Syntax- C:\> EDIT <File name>
Example- C:\> Edit NIST
Syntax- C:\> LABEL
Syntax- C:\>More <File Name>
Example-C:\>More NIST
Syntax- C:\>MEM
Syntax- C:\> CHKDSK
Syntax-C:\> ATTRIB <Switch> <file name>
Some switches are as follows-
+H - Make hidden file
-H - To turn the file back in to normal mode.
+R - To set the file in to read only mode.
-R - To turn the file back in to normal from.
TREE This command graphically displays the path of each directory and subdirectory on the give drive.
Syntax-[1.]C:\> TREE
[To view the name and paths of all directories and subdirectories on you system.]
[2.] C:\> TREE/F
[To view file name along with the Directory/ Subdirectory name.]
Syntax- C:\>Edit <File name>.BAT
Autoexec.Bat Autoexec.Bat is a special batch file that executed automatically when you power up the system or reset it. It can also be executed from Dos by typing Autoexec.
Syntax- C:\>Copy Con Autoexec.Bat
Or C:\>Edit Autoexec.Bat